Cyber security & crimes
Guidance on cyber security tactics, what are cyber-crimes and crime reporting
What are cyber security and crimes?
Cyber security is a collection of technical controls and human protocols, which are designed to protect organisations and individuals from the actions of criminals.
Cyber-crime is a way of committing crimes via computers and their networks. This may be to steal people’s identities or business secrets, to commit fraud or for other exploitative or malicious purposes.
This article covers four main themes:
- How to report a cyber-crime
- The scope of cyber-crimes
- The technical aspects of cyber security
- The human dimension of cyber security
1. Reporting a cyber-crime
The main way of reporting cyber-crime in the UK is through the National Fraud and Cyber Reporting Centre – Action Fraud website and telephone line.
There is also the National Crime Agency's National Cyber Crime Unit (NCCU), for more serious cyber security threats.
The NCCU leads the UK’s response to cyber-crime, supports partners with specialist capabilities and coordinates the national response to the most serious of cyber-crime threats.
They work closely with the Regional Organised Crime Units (ROCUs), the Metropolitan Police Cyber Crime Unit (MPCCU), partners within Industry, Government and International Law Enforcement.
And here is another related link which you may find useful.
Scam marshals
A Scam Marshal is any resident in the UK who has been targeted by a scam and now wants to fight back and take a stand against scams.
2. The scope of cyber-crime
Cyber-crimes are typically done for financial gain or malicious purposes. One example of this is identity theft.
Identity theft video - click to play
And with an increasing number of electronic devices both in the home and at work connected to computer networks, the security risks are spread far beyond desk-top computers.

So what steps can you take to avoid becoming a victim of cyber-crime? Here are some suggstions.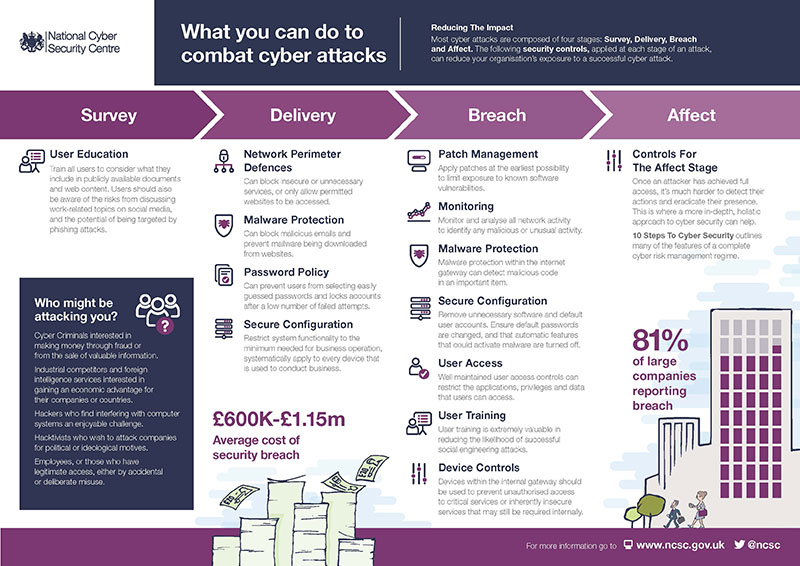
2. The scope of cyber-crime
Cyber-crimes are typically done for financial gain or malicious purposes. One example of this is identity theft.
Identity theft video - click to play
And with an increasing number of electronic devices both in the home and at work connected to computer networks, the security risks are spread far beyond desk-top computers.

So what steps can you take to avoid becoming a victim of cyber-crime? Here are some suggstions.
3. Cyber security – technical controls
Here is a high-level guide to things you can do to reduce the risk of cyber-crime.
- Secure your Internet connection
- Secure your devices and software
- Control access to your data and services
- Protect from viruses and other malware
- Keep your devices and software up to date
4. Cyber security – a human dimension
Even with the most sophisticated technical cyber security controls, people are often the weakest link in the cyber security chain. This is why making people aware of the risks of cyber-crime, and offering them training in organisations is so important.
10 Step User Education & Awareness
Here are some more guidelines for people in your organisation:
Email communications
- Emails are like postcards – if you wouldn’t put it on a postcard, don’t put it in an email.
- Ensure you have the correct recipient before sending information.
- Emails have the same standing in law as other written communication
- Never initiate of forward spam or chain type emails
- Never send work related documents to your personal email account
- Don’t use your work email address for personal subscriptions to websites
Phishing emails
Phishing is the use of fraudulent emails to steal your information.
- Be wary of emails from unknown senders, especially when they ask you to confirm information.
- Never click links or open attachments from emails that you are not expecting.
- If a colleague asks you to send them something via email, confirm via phone before you do.
- If in doubt, contact your IT department and get it checked out.
Internet – staying safe online
- Never connect with people you don’t know.
- Never post personal information such as your address, date of birth or bank details.
- Never discuss work related issues on social media.
- Never share personal or sensitive information online, especially with strangers.
- Never upload compromising or work related photos.
- Publin WiFi is not secure. Don't use it to share personal or sensitive information.
Password protection


Give information
Give information anonymously by phone on 0800 555 111 or online

Donate to us
Join our fight against crime by making us a donation today, and see how the money you give can help shape your community for the better.

Volunteer
Every year we stop thousands of crimes. Let’s help make communities safer together. Join us and start volunteering with your local Crimestoppers team today.
